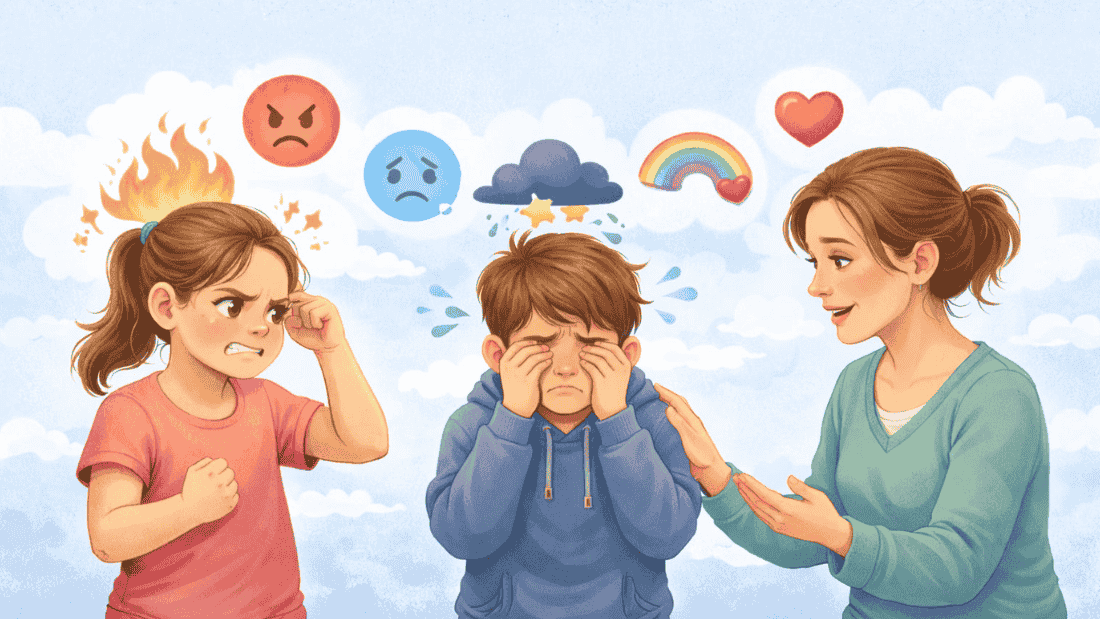
Meltdowns, mood swings, and emotional shutdowns are often misunderstood as behavioral problems. In reality, they are frequently signs that a child or teen is still learning emotional regulation – a critical life skill.
What Is Emotional Regulation?
Emotional regulation is the ability to:
- Recognize emotions
- Understand what they mean
- Manage responses in healthy ways
Children are not born with this skill, it develops over time with guidance, safety, and modeling.
Why Emotional Regulation Is So Hard for Kids and Teens
- Developing brains
- Hormonal changes in adolescence
- Stress, anxiety, or trauma
- Academic and social pressure
Teens, in particular, experience intense emotions before their impulse control systems are fully developed.
Common Signs of Emotional Dysregulation
- Explosive reactions
- Emotional shutdown or withdrawal
- Difficulty calming down
- Overreacting to minor stressors
- Trouble expressing feelings with words
How Parents Can Support Emotional Regulation
- Name emotions (“It looks like you’re feeling frustrated.”)
- Stay calm during big feelings
- Teach coping tools (breathing, movement, journaling)
- Focus on connection before correction
A child psychiatrist can help identify whether emotional struggles are developmentally typical or linked to anxiety, ADHD, mood concerns, or other factors.
Long-Term Benefits of Emotional Skills
Children who learn emotional regulation are more likely to:
- Handle stress effectively
- Build healthy relationships
- Develop confidence and resilience
Big feelings are not a problem – they are an invitation for support, skill-building, and growth.

Leave A Comment